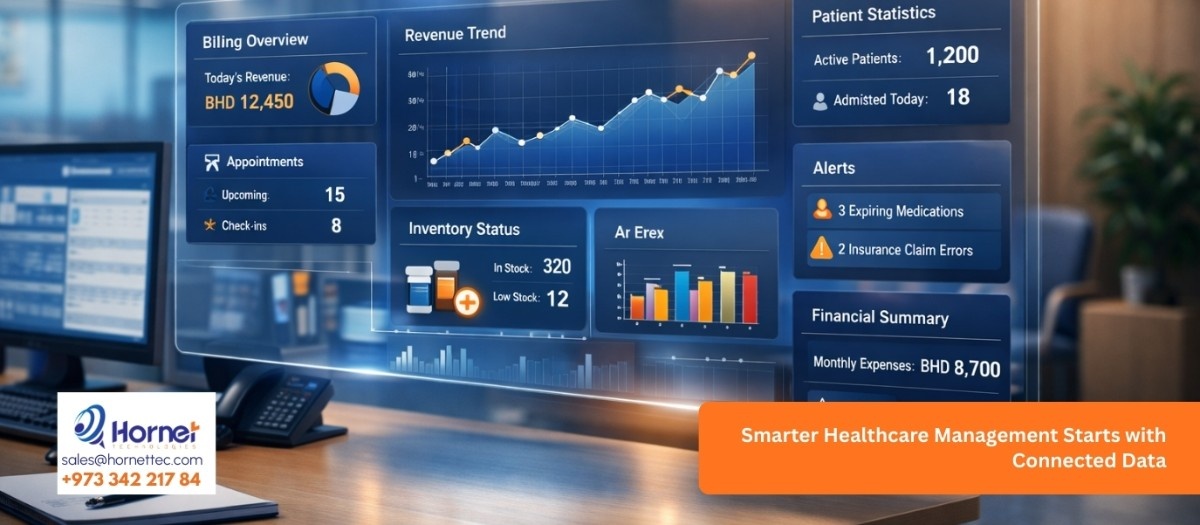
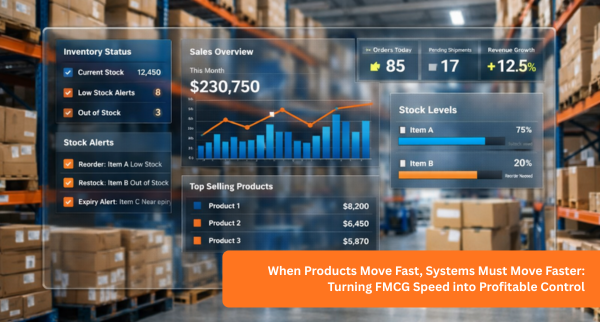
In pharmaceutical operations, control is not optional. Every batch produced, stored, or distributed carries responsibility. And when batch numbers, expiry dates, or recall data are not clearly connected, small gaps turn into serious risks.
For pharma manufacturers and distributors across Bahrain and the GCC, this challenge becomes sharper as operations scale. More products. More locations. More audits. More pressure.
This is where ERP-driven pharma operations stop being “nice to have” and start becoming essential.
What ERP-Driven Batch Control Means in Pharmaceutical Operations
ERP-driven batch control is a shift from manual record-keeping to a unified digital system that automates the assignment, tracking, and tracing of every pharmaceutical batch from raw material receipt to final sale. Key features include enforcing compliance by blocking expired stock at dispatch, automating Electronic Batch Records (EBRs), and enabling bi-directional traceability for rapid, targeted recalls.
Pro-Tip
Unified systems don't just record data; they actively prevent non-compliant actions before they happen.
Why Batch, Expiry, and Recall Control Matters More in GCC Pharma Operations
Pharma businesses in the GCC operate in a tightly regulated environment.
Audits are frequent. Documentation is mandatory. Traceability is assumed, not requested.
At the same time, many companies grow faster than their internal systems.
⚠️ New SKUs are added quickly.
⚠️ Distribution expands across multiple warehouses or countries.
⚠️ Manual checks stay the same.
The result is not failure overnight. It is gradual loss of visibility,
until something goes wrong.
This blog focuses on how ERP helps prevent that situation before it becomes costly.
Market Insight: Pharmaceutical ERP Growth
According to DataIntelo, the global pharmaceutical ERP software market was valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach around USD 5.9 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.8%. This growth reflects a clear shift toward centralized systems that can handle batch traceability, expiry control, and compliance demands at scale.
Research Source
Where Batch and Expiry Management Usually Breaks
Most pharma companies do not start with poor processes. Problems appear when growth exposes system limits.
- Common Breakdown Points
- Root Cause Analysis
- Consequences
- Batch records living in production systems, while inventory lives elsewhere.
- Expiry dates checked manually during dispatch instead of being system-controlled.
- No single view of where a batch has moved once it leaves the warehouse.
- Difficulty answering simple audit questions quickly.
- Panic and confusion when a recall notice arrives.
The root cause of breakdowns in batch and expiry management typically stems from:
- Fragmented Systems: Different departments using disconnected software solutions.
- Manual Processes: Reliance on spreadsheets, paper records, and human memory.
- Lack of Integration: Inability to share real-time data across the supply chain.
- Scalability Gaps: Systems that worked for small operations fail when volume increases.
When batch and expiry management breaks down, the consequences extend beyond operational inefficiency:
- Regulatory Penalties: Fines and sanctions from authorities like SFDA and NHRA.
- Product Recalls: Costly withdrawals that damage brand reputation.
- Patient Safety Risks: Potential distribution of expired or contaminated products.
- Financial Losses: Write-offs of expired inventory and lost sales.
- Audit Failures: Inability to provide required documentation during inspections.
What ERP Changes at a Process Level
ERP does not “add another tool.” It replaces fragmented tracking with a single operational flow.
Batch creation, inventory, quality, and dispatch share one data source. This eliminates discrepancies between departments and ensures everyone works with the same information.
Expiry logic is built into daily transactions. The system automatically applies FEFO (First Expired, First Out) rules during picking and dispatch, preventing human error.
Movement of stock is traceable across locations and customers. Every transfer, sale, or return is recorded against the specific batch, enabling full forward and backward traceability.
Controls happen automatically, not through reminders or follow-ups. The system blocks non-compliant actions before they occur, such as shipping expired products.
This shift is what makes control sustainable, especially when ERP-driven operations are designed around pharma-specific workflows rather than generic system setups.
Academic Research Supports ERP Adoption
A 2023 research paper published in the AIP Conference Proceedings highlights that pharmaceutical companies increasingly rely on ERP systems to coordinate information across departments using a shared database, enabling what the authors describe as a “consolidated view” of operations. The study also notes that ERP adoption significantly improves real-time visibility, quality control, and decision-making, especially in highly regulated pharmaceutical environments.
Batch Number Management From Production to Distribution
Batch numbers are the backbone of pharma traceability. ERP treats them as first-class data, not reference fields.
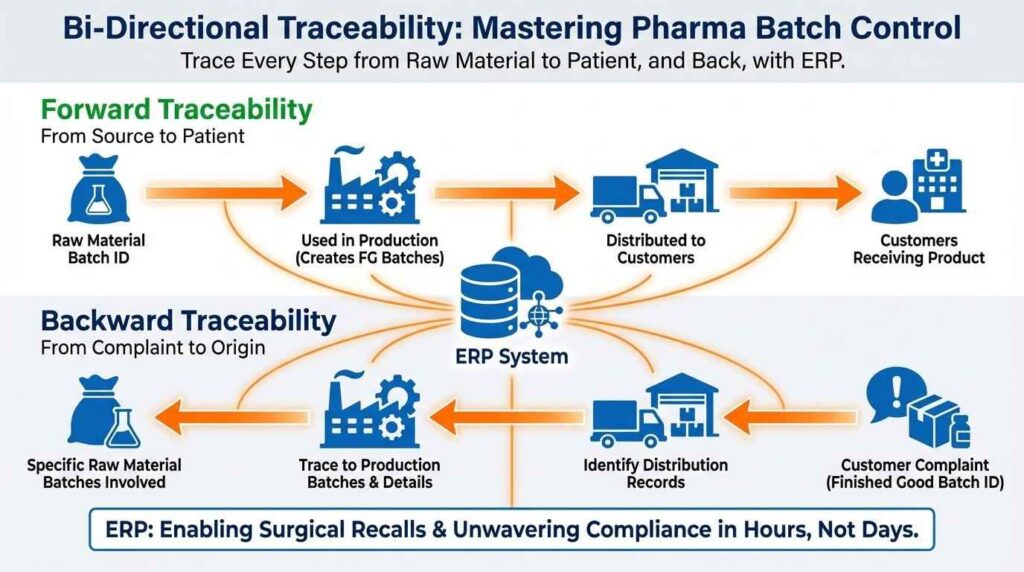
Automated batch tracking ensures complete traceability from production to patient
With ERP:
- Batch numbers are generated automatically during manufacturing or receipt.
- Digital batch records replace paper files and spreadsheets.
- Every movement is recorded against the batch.
- Forward tracing shows where a batch went.
- Backward tracing shows what went into it.
Even when batches are split, merged, or transferred, traceability remains intact.
This matters during audits. It matters even more during recalls.
Batch Traceability and Serialization in GCC Pharma Supply Chains
High Stakes
Pharmaceutical inventory is a liability if not managed correctly. In the GCC, stringent oversight from authorities like the SFDA (Saudi Arabia) and NHRA (Bahrain) increases the pressure.
Regional Challenges
Operations in the GCC face growing market demand and tightening regulations, managing thousands of SKUs across multiple locations.
Relying on human vigilance for expiry and batch tracking is a systemic failure, as human error is a root cause in over 80% of process deviations in pharma. Inadequate control jeopardizes patient safety, damages brand reputation, and leads to significant financial losses.
Ready to Transform Your Pharma Operations?
Discover how Hornet Technology’s ERP solutions can help you achieve complete batch control, automated expiry management, and recall readiness. Schedule a personalized demo today.
Source: https://dataintelo.com/report/pharmaceutical-erp-software-market
Expiry Date Management That Prevents Loss Before It Happens
Expiry management fails when it is treated as a reminder task. ERP changes this by making expiry a control rule, not a warning.
Automated FEFO Logic
First Expired, First Out (FEFO) logic applied automatically during picking
and dispatch, ensuring proper stock rotation without manual intervention.
System-Level Blocks
Automatic blocks on expired or near-expiry stock prevent accidental dispatch, eliminating compliance risks and protecting patient safety.
Proactive Alerts
Early warnings for slow-moving or short-expiry batches allow proactive management, reducing write-offs and maximizing inventory value.
Instead of discovering loss at month-end, teams see it early and act.
Recall Readiness Without Chaos
Recalls are not frequent. But when they happen, response time defines the damage. ERP-driven recall handling focuses on precision.
A structured recall process includes:
- Identifying the affected batch within hours.
- Tracing where it was stored, sold, or transferred.
- Isolating only impacted stock, not entire product lines.
- Generating recall reports directly from system data.
- Maintaining a full action trail for audit review.
This turns recall response from firefighting into execution.
Staying Audit-Ready Without Last-Minute Scramble
Audits become stressful when data has to be “assembled.” ERP removes that pressure.
- Every transaction is time-stamped.
- Changes are logged automatically.
- Batch history is accessible in one place.
- Quality approvals are linked to inventory movement.
- Reports are generated without manual consolidation.
Audits shift from disruption to routine.
With ERP, your operation is always audit-ready, with complete documentation available at the click of a button.
How ERP Supports Both Manufacturers and Distributors
Pharma supply chains do not work in isolation. ERP reflects that reality.
For Manufacturers
- Strong batch integrity from raw material to finished goods.
- Faster batch release through digital records.
- Fewer deviations caused by missing data.
For Distributors
- Batch-wise visibility across all storage locations.
- Expiry-aware dispatch and returns.
- Faster response to manufacturer-led recalls.
One system supports both roles without duplication.
Business Outcomes That Matter
When batch, expiry, and recall processes are system-driven, results follow naturally.
Reduced Write-offs
Significant decrease in expired stock write-offs through proactive expiry management.
Targeted Recalls
Smaller, targeted recalls instead of costly blanket withdrawals.
Faster Audits
Reduced audit cycle times with readily available documentation.
Confident Teams
More confident teams during inspections with system-backed compliance.
Scalable Growth
Ability to scale operations without adding proportional manual checks.
Predictable Control
Consistent operational control independent of individual vigilance.
Control becomes predictable.
What to Evaluate Before Relying on ERP for Pharma Control
Not every system delivers this level of discipline. Before relying on ERP, ask:
Cross-Location Tracking
Can it track batch movement across all locations?
Active Expiry Control
Does expiry logic actively block incorrect dispatch?
Bidirectional Traceability
Is recall tracing both forward and backward?
System-Enforced Audits
Are audit trails enforced by the system?
Quality Integration
Can quality status stop inventory movement?
Critical Insight
If the answer to any of these questions is unclear, risk remains in your pharmaceutical operations. A comprehensive ERP solution should address all these points without exception.
Final Takeaway
Batch numbers, expiry dates, and recalls are not edge cases in pharma. They are daily operational realities.
ERP-driven pharma operations make control consistent, not dependent on individuals or manual checks.
For pharma manufacturers and distributors in Bahrain and the GCC, this level of readiness is not about technology adoption. It is about operational confidence as the business grows.
If your operations are scaling, your control systems must scale with them.
Take Control of Your Pharma Operations Today
Don’t let manual processes and fragmented systems put your compliance at risk. Discover how Hornet Technology’s ERP solutions can transform your batch management, expiry control, and recall readiness.